Table of Contents
Safeguarding sensitive information is a pressing concern for individuals and organizations alike. With cyber threats on the rise, traditional authentication methods are proving insufficient in protecting against unauthorized access. Multifactor authentication (MFA) offers an extra layer of security beyond passwords. But with numerous MFA methods available, choosing the best multifactor authentication solution can be daunting. In this guide, we explore the different MFA types, their strengths, weaknesses, and key considerations to help users find the best fit for their security needs.
All types of MFA are not created equal and Not all MFA methods are the same.
What is Multifactor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security method that requires users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access to a system, application, or data. The importance of MFA lies in its ability to significantly enhance security and protect against various cyber threats, including password breaches, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access attempts.
 What is the difference between 2 step (2FA) and multifactor authentication (MFA)?
What is the difference between 2 step (2FA) and multifactor authentication (MFA)?
2FA and MFA are sometimes used interchangeably but there are some nuanced differences:
- 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication): Requires two authentication factors to authenticate. In some cases, you are able to use the same authentication factor like a password and PIN (Something you know).
- MFA (Multifactor Authentication): Requires two or more different authentication factors to authenticate. Like 2FA, you can start with a username and password, but will need additional authentication factors like a cellphone (something you have) or biometric fingerprint scan (something you are).
All 2FA is MFA but not all MFA is 2FA. Technically, MFA is more secure than 2FA since it allows for more authentication factors but it is not always the case. The authentication factors used and their overall strength are the most important when determining which method is stronger. We will address authentication factors and their security rankings below.
What are the three main authentication factors?
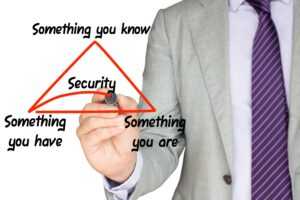
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) combines two or more authentication factors from three different main categories:
- Something you know (knowledge), like a username, password, or PIN
- Something you have (possession), like a smartphone, token, or smart card
- Something you are (inherence), like fingerprints, iris scan, or voice/facial recognition
By combining two or more of these factors, MFA adds an extra layer of security beyond just a password, making it significantly more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access. Requiring multiple factors for authentication mitigates the risk of account compromise and data breaches, helping organizations safeguard sensitive information, maintain regulatory compliance, and preserve user trust.
According to Microsoft, Google, and SANS Software Security Institute, MFA can block over 99.9 percent of automated attacks aka bot attacks SANS Institute.
 Benefits of Multifactor Authentication: Why MFA is Important
Benefits of Multifactor Authentication: Why MFA is Important
- Enhanced Security: MFA strengthens security by requiring multiple authentication factors, reducing unauthorized access risks.
- Mitigating Credential Theft: It counters credential theft by adding layers of protection beyond passwords.
- Compliance Requirements: MFA is essential for meeting compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and more.
- Protecting Against Unauthorized Access: It provides additional layers of defense against unauthorized access.
- Securing Remote Access: MFA is crucial for securing remote access, especially in prevalent remote work environments.
- Cost-Effective Security Measure: Implementing MFA is a cost-effective solution compared to post-breach repercussions.
Types of Multi-Factor Authentication and Their Security Rankings
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each type of Multifactor Authentication is important when implementing effective cybersecurity measures. Below is our ranking of the different multifactor authentication (MFA) methods from strongest to weakest:
Hardware Tokens
Hardware tokens are physical devices that generate one-time passwords (OTPs) or cryptographic keys. They are among the most secure MFA methods because they are not vulnerable to online attacks such as phishing or malware. However, they may be less convenient than other methods and could be lost or stolen.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint scanning, iris recognition, or facial recognition, are highly secure as they rely on unique physical characteristics of the user. While biometric data could potentially be spoofed or compromised, it requires significant effort, making it a robust authentication option.
 Smartphone Authenticator Apps
Smartphone Authenticator Apps
There are two types of MFA on smartphone apps. They offer a higher level of security compared to SMS-based methods as they do not rely on the cellular network and are less susceptible to interception. However, they are still vulnerable to phishing attacks if users are tricked into revealing the generated codes
Time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs)
Authenticator apps generate a 6-8 digit code once every 30 seconds. The user needs to input this code before the code expires to authenticate.
Push notifications
Once you reach the MFA portion of your login, you will be sent a push notification to your smartphone. You need to simply input the 2-digit code (Microsoft Authenticator) or press “yes” (Google Authenticator) to complete your login. If you take too long to complete this step, it will time out and you may need to send another push notification to your phone.
SMS-based Authentication
SMS-based authentication involves sending a verification code to the user’s mobile phone via SMS. While better than single-factor authentication (password-only), SMS-based MFA is susceptible to various attacks such as SIM swapping, SMS interception, and phishing. It’s less secure compared to authenticator apps and biometric authentication.
Email-based Authentication
Email-based authentication sends a verification code to the user’s email address. This method is generally considered less secure than SMS-based authentication because email accounts are often targeted by attackers and may have weaker security measures in place. This method is the most insecure and is only slightly better than not having MFA at all. This should never be your only method of MFA.
 What is the Best Multifactor Authentication Solution? What We Recommend
What is the Best Multifactor Authentication Solution? What We Recommend
Although MFA can greatly increase the security posture of an organization, achieving a balance between end-user effort and security is also important. Adding too many layers and steps can sometimes cause inconvenience and user frustration. In our years of experience, we’ve found that administrators must strike a balance that is robust and user-friendly. For example, email MFA can be both tedious and insecure while swiping a smart card may be easy but can be stolen by malicious actors.
Why we use Smartphone Authenticator Apps
These days, almost everyone has a smartphone, which easily satisfies the “something you have” authentication factor listed above. These apps often come with an additional layer of protection requiring a PIN or biometric authentication in case a malicious actor gets physical access to your phone. They generate push notifications locally on the user’s device, reducing the risk of interception or phishing attacks. They also offer integration with identity providers, making them suitable for a wide range of business applications.
Our Top 3 Recommended Authenticator Apps for MFA
Microsoft Authenticator:
- Supports Time-Based One-Time Passwords (TOTP) and push notifications for authentication.
- Multi-device support, allowing users to seamlessly switch between devices.
- Integration with Microsoft accounts and other services for secure authentication.
- Backup and recovery options for accounts.
- Enhanced security features such as biometric authentication and device health checks.
Google Authenticator
- Generates Time-Based One-Time Passwords (TOTP) for two-factor authentication.
- Simple and straightforward user interface.
- Works offline, keeping generated codes stored locally on the device.
- Secure and reliable authentication method widely used by various services.
- Limited functionality beyond basic TOTP generation.
Authy
- Supports Time-Based One-Time Passwords (TOTP) and push authentication methods.
- Multi-device support, allowing users to sync accounts across multiple devices securely.
- Encrypted backups for account recovery, ensuring users can access their accounts if they lose their device.
- User-friendly interface with customization options for organization and categorization of accounts.
- Additional security measures such as PIN protection and biometric authentication.
Summary
As a managed service provider committed to safeguarding your assets, IntegriCom is well-equipped to help you navigate the diverse landscape of MFA methods by assessing their security rankings and tailoring solutions to your specific needs. From biometrics to hardware tokens, empower your organization against cyber threats by implementing robust MFA measures. Contact us now to elevate your cybersecurity posture and protect your valuable assets with confidence.
Enhance Your Security with IntegriCom Managed IT Services
IntegriCom provides managed IT Services and can manage all your security needs. Please contact us for a free evaluation. We can provide a complete security assessment of your total environment and provide a remediation report and recommended support options.


